Determine the bond order of the #"C"-"O"# bond in the following molecules, and then arrange the #"C"-"O"# bond lengths in increasing order? #"CO"#, #"CO"^(+)#, #"CO"^(2+)#, #"CO"_2#, #"CO"_3^(2-)#
1 Answer
Bond length increases from left to right on your list, i.e.
#r_(CO) < r_(CO^(+)) < [r_(CO^(2+)) = r_(CO_2)] < r_(CO_3^(2-))#
#"CO"# :#3# #"CO"^(+)# :#2.5# #"CO"^(2+)# :#2# #"CO"_2# :#2# #"CO"_3^(2-)# :#1.bar(33)#
In order to determine this, we should reference an MO diagram.
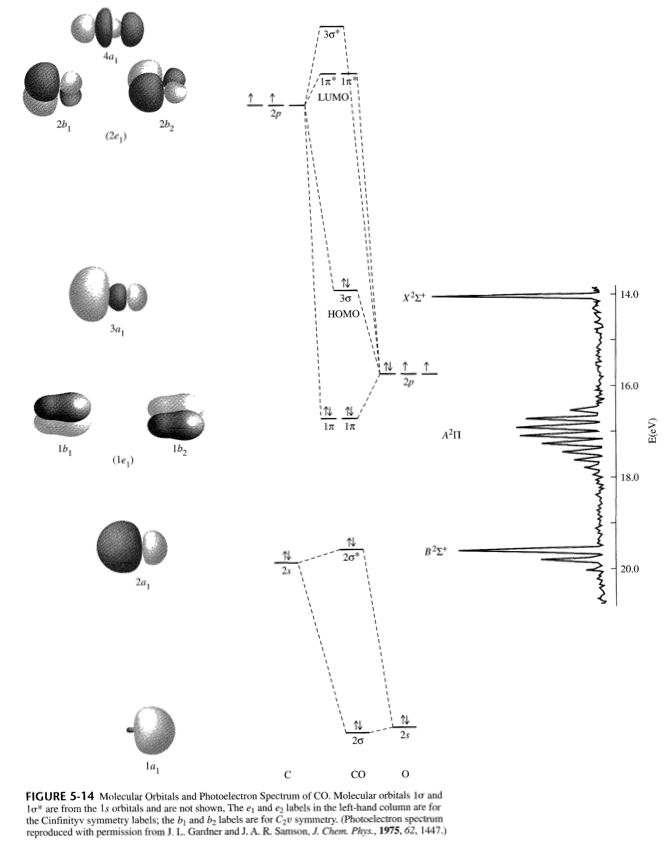
We can see that the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) is fully occupied, but the next-highest MOs are the
CO MOLECULE
#"BO" = 1/2("Bonding - Antibonding")#
#= 1/2([stackrel(2sigma)overbrace(2)+stackrel(1pi)overbrace(2(2)) + stackrel(3sigma)overbrace(2)] - [stackrel(2sigma^"*")overbrace(2)]) = 3#
CO+ CATION
CO
CO2 MOLECULE
#:stackrel(..)("O")="C"=stackrel(..)"O":#
So, its double bonds suggest a bond order of
CARBONATE ANION
By considering its resonance delocalization, the bond order on this molecular ion can be determined.
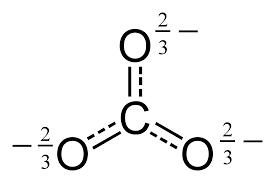
We should notice that for the
Since perfect single bonds have a bond order of
OVERALL
Overall, we have the bond orders:
#"CO"# :#3# #"CO"^(+)# :#2.5# #"CO"^(2+)# :#2# #"CO"_2# :#2# #"CO"_3^(2-)# :#1.bar(33)#
You can choose how to order
Hence, bond length increases down this list.

