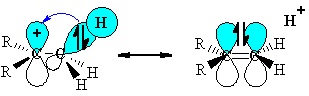What is hyperconjugation?
1 Answer
Hyperconjugation is an extended delocalization of electron density from a
A common instance of this occurs in organic chemistry on carbocations.
Adjacent alkyl groups contain
Thus, the more alkyl groups around the carbocation (e.g. the more substituted the carbocation), the more stable it is, i.e.
#3^@ > 2^@ > 1^@ > "methyl"# #"carbocation"# ,
the tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary, which is more stable than the primary, which is more stable than the methyl carbocation.